Industrial Battery Watering Methods and Best Practices
- May 8, 2019
- Uncategorized
- Posted by pennwesthost
- Leave your thoughts
The battery for your electric lift truck is designed to give you power for 5 years and even longer.
The maintenance is easy if you have the proper knowledge. Flooded Lead Acid batteries are still the most reliable and most environmentally friendly power sources available. Your battery is almost 100% recyclable. Lead and Copper go to secondary smelters. Plastic is recycled and even the acid is separated and refined to later be used in fertilizers, cleaners, and purifiers in alkalia based materials.
Your battery has a Life Cycle. The life cycle is based on usage (Energy Out) and Charge (Energy In). One discharge and subsequent complete charge constitutes one cycle. Therefore, if you fully discharge and recharge your battery every day the life cycle of your battery is approx. 5 years. (1,500 Cycles / 300 working days a year. Every situation varies and the 1,500 cycle measurement is not absolute. Once 1,200 to 1,500 cycles is reached the battery will begin to provide less power than it once did when it was new. This translates into run time for your forklift. What was once a 6 hour per charge run time of constant work can drop to 5 hours or perhaps even less based on the quality of the battery and the care that has been given to the battery. You want you battery to last well past the time where it begins to restrict your companies productivity and so do we. This can only be done with care from day one. The following covers battery watering. The over-watering or lack of watering the battery is the number one cause of pre-mature failures.
Battery Watering
A battery should only be watered after it has been fully charged.
Adding water to a fully charged battery should be done with either purified city water, distilled water, or water purified through a De-Ionized Filtering System. Water from a well are non-purified system can harm a battery due to the many inherent by products such as calcium, lime, iron and sulphur.
The water should be added to a level of ¼” over the splash plate. This will ensure that the plates of the battery are covered.
DO NOT add water if the water is already at this level. A fully charged batteries water is at its highest point once a charge is complete. Over watering causes corrosion to form on the battery surface because the water level is raised during the charging process causing it to overflow and contact the batteries steel case.
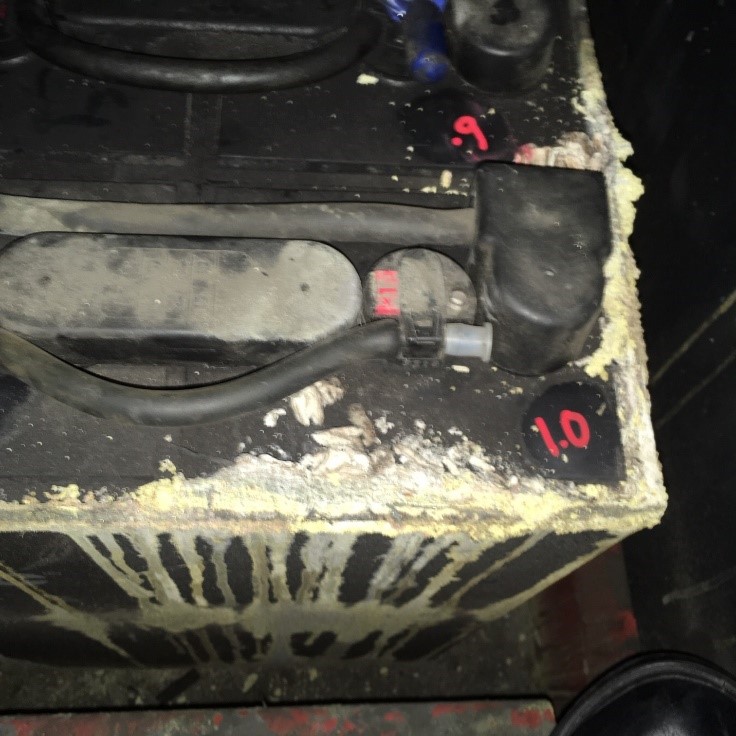

The above photo shows a 3-year-old battery that was not properly watered. Over watered due to a malfunctioning watering system.
You can see the corrosion build up along with the checked cell voltage. This battery had an average voltage of .90 to 1.50 volts per cell. It should be reading 2.10 to 2.25 volts per cell after a full charge and its age. The Sulphur acid or Electrolyte had become so diluted that it could no longer charge to an acceptable voltage. In addition, the heat generated by the charger to obtain the proper voltage during a charger ended the batteries life. This battery required replacement due to severe misuse.
There are several safe and inexpensive ways to water your battery. REMEMBER to be safe when you do it and wear protective gear.
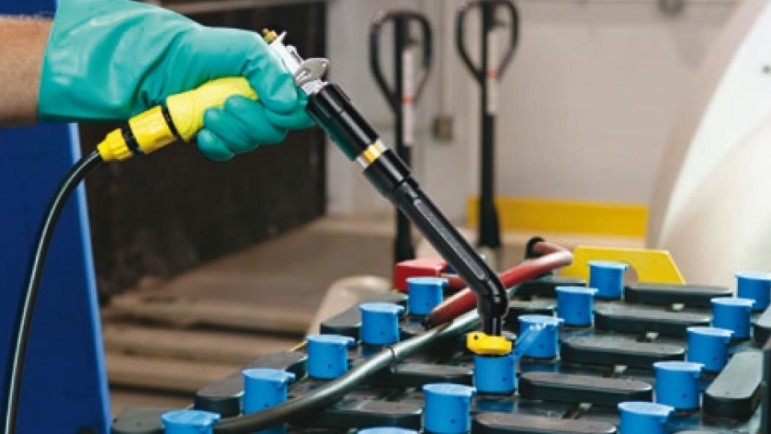


It always pays in the long run to get helpful advice. PennWest can offer several solutions on which best suits your budget and needs. You may also wish to utilize a safe alternative as a Single Point Watering System that can be install on your battery by Pennwest Toyota Lift. Flow-Rite is one of the most reliable and versatile systems available.

The Millennium EVO Battery Watering System makes the difficult task of watering industrial batteries elementary. It consists of automatic shut-off valves, interconnected with tubing, that replace the existing vent caps. A quick coupling allows the system to be connected to a water supply. Once connected, water flows into each cell until it reaches the correct level. A flow indicator built into the water supply tells the operator when filling has been completed. The entire process takes just 30 seconds per battery.
Cost Savings After installing your Millennium Plus+ system, you will realize other cost benefits including extended battery life; increased performance; and cleaner floors, equipment and battery tops.
Safety Fill batteries without having to remove the vent covers. Avoid battery acid burns, ruined clothing, and noxious fumes. Add optional flame arrestors to prevent ignition of flammable battery cell gasses.
Extend Battery Life & Performance A properly watered battery lasts longer and performs better. Overfilling a battery results in loss of acid, while charging with low electrolyte levels will result in permanent damage to the lead plates. Both will result in loss of capacity and life expectancy.
Time saving convenience Snap on/snap off water connections and fast filling turn the often ignored task of watering batteries into a quick, simple task allowing you to fill each battery in 30 seconds or less!
Pennwest can assist you with all aspects of the materials, installation and training. Please see the attached product offering reviewing the Flow-Rite. You may also wish to consider our semiannual battery and charger testing cleaning and maintenance. Very comprehensive and affordable to make sure that you are getting the most out of your investment.
A certain amount of water loss is normal in all batteries and it should be replaced with “pure” tap or distilled water. In some areas around the country, tap water may contain chemicals or other impurities harmful to batteries. If water is needed, add just enough to bring the electrolyte to the proper level. Batteries should be filled only at the end of the charging cycle. Overfilling is the most common error made when watering and it can cause tray corrosion. Since tray corrosion can cause extensive damage to batteries and vehicles, extreme caution must be taken to avoid overfilling the batteries.
Tray Corrosion
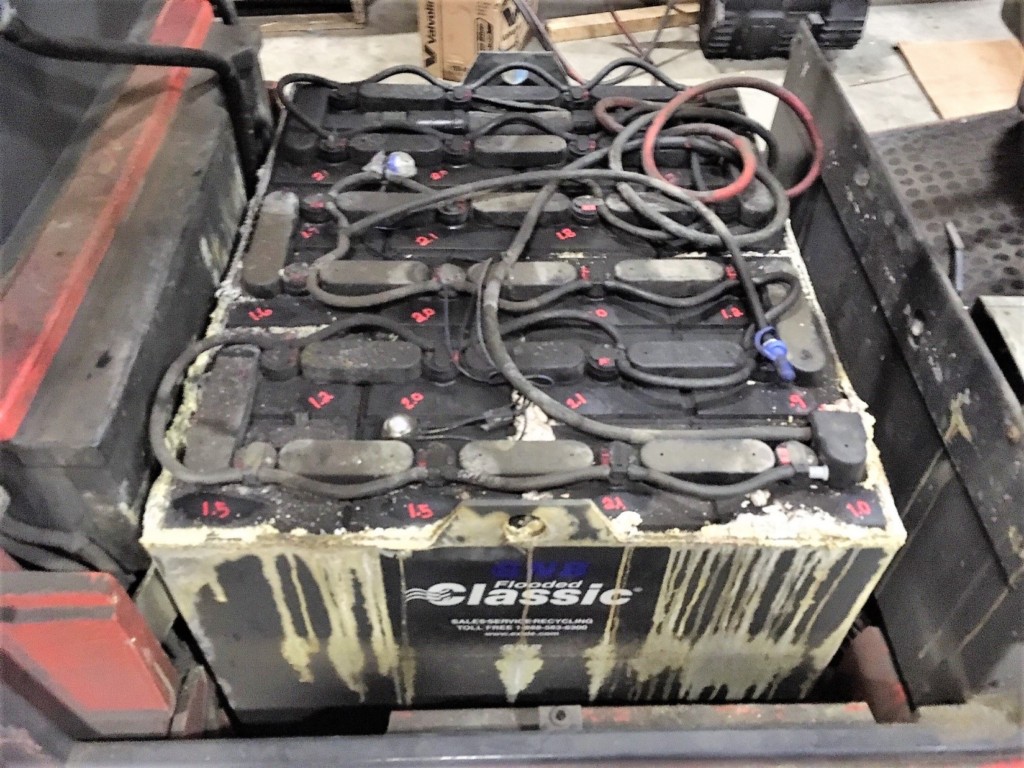

Motive power battery trays are mostly made of steel that is protected with an acid resistant coating. Regardless of how good the coating is, if a break in the coating exposes the steel tray to sulfuric acid spilled from the battery, the acid will corrode the tray. How quickly the tray corrodes depends on how much and how often acid is spilled on top of the battery and how often the battery is cleaned.
The major cause of tray corrosion is overwatering or overfilling a battery. When overfilled, the electrolyte will spill on top of the battery. Although the water in the electrolyte will evaporate, the highly concentrated acid solution remains and gives the appearance of dampness. If the acid is not removed, the tray will eventually corrode. To prevent corrosion, batteries should be cleaned any time the accumulation of dampness or acid becomes significant.
Battery Watering Schedule
Lowe electrolyte level in a cell can cause the plates to oxidize and shorten the life of the cell and the battery. To prevent, water should be added often enough to keep the electrolyte level above the perforated separator protectors. Ideally a watering policy or schedule should be adopted and followed strictly. One of two systems can be used. In the first, the electrolyte level of two or three cells is checked each time the battery is changed. In the second, water is added to all of the batteries assigned to each charging area on a regular time schedule. The electrolyte levels are also spot checked periodically to determine if the proper levels are being maintained. Determining a reasonable and proper battery watering time schedule could be easy or difficult, depending on how widely the following three factors vary:
- Frequency of charge (daily, three times a week, etc.).
- Water storage capacity of the specific cell type.
- Age and condition of the battery
Older batteries and those in poor condition will consume water more rapidly than newer batteries and those in good condition. Also some cell types have a greater water storage capacity than others. Depending on the preceding variable factors, the batteries assigned to a specific charging area will require watering at different intervals. The frequency of watering is best determined by first‐hand experience. Example: if some batteries have low electrolyte levels when a weekly watering schedule is followed, change the schedule to twice a week.




